T Cell Assays
RoukenBio's T cell assays are designed to provide deep insights into T cell functionality, activation, and engineering. Our T cell assays support detailed evaluation of T cell biology across multiple therapeutic modalities.

Why T cells?
T cells are central players in the adaptive immune system, able to directly kill malignant or infected cells as well as coordinate the wider immune response (cytotoxic and helper T cells respectively). These functions combined with their antigen-specific nature and ability to form immunological memory make T cells attractive therapeutic targets. We offer an extensive suite of T cell assays to support cutting-edge immunological research and therapeutic development. Our assays are designed to provide deep insights into T cell functionality, activation, and engineering, forming a robust foundation for any T cell activation assay or downstream functional study.
Access our extensive suite of T cell assays
T Cell Activation
T Cell Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity
T Cell Polarisation
Treg Assays
T cell Exhaustion
Gamma-Delta T Cell Assays
T Cell Depletion Assays
CAR-T Cell Engineering
T Cell Activation
Evaluate the activation of T cells through the measurement of activation markers, cytokine production, and proliferation in response to antigenic, allogeneic or pharmacological stimuli applicable to basic immunological research, vaccine development, and therapeutic screening. At RoukenBio we are well versed in a variety of T cell stimulation assays and can advise on those most applicable to your research:
- Antigen specific assays – antigen recall using pre-screened donors e.g. CMV, expansion and banking of rare populations of antigen specific T cells for use in various downstream applications (e.g. MART1-specific T cells in TDCC assays), TCR transduction to create banks of antigen specific primary T cells or even reporter cell lines.

PBMC from a CMV+ donor were stimulated with CMV lysate in the presence of infliximab (anti-TNF-α) or nivolumab (anti-PD-1). Infliximab induced a dose-dependent inhibition of proliferation in both CD4 and CD8 T cells and a reduction in IFNγ production. Nivolumab induced a dose- dependent enhancement of proliferation in both CD4 and CD8 T cells and an increase in IFNγ production.
- Polyclonal – several classes of polyclonal activator can be employed in our assays, from plant-derived lectins such as phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and concanavalin A (ConA), to various anti-CD3/CD28 antibody based formats, we can advise on those best suited to your study.
Mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) – based on the reaction to mismatched HLA between unrelated donors, the stimulation of T cells by allogeneic PBMCs or monocyte-derived dendritic cells represent a flexible platform for assessment of immunomodulatory compounds. This is often used as a T cell activation assay system for immunomodulator profiling.

T Cell Activation
Evaluate the activation of T cells through the measurement of activation markers, cytokine production, and proliferation in response to antigenic, allogeneic or pharmacological stimuli applicable to basic immunological research, vaccine development, and therapeutic screening. At RoukenBio we are well versed in a variety of T cell stimulation assays and can advise on those most applicable to your research:
- Antigen specific assays – antigen recall using pre-screened donors e.g. CMV, expansion and banking of rare populations of antigen specific T cells for use in various downstream applications (e.g. MART1-specific T cells in TDCC assays), TCR transduction to create banks of antigen specific primary T cells or even reporter cell lines.

PBMC from a CMV+ donor were stimulated with CMV lysate in the presence of infliximab (anti-TNF-α) or nivolumab (anti-PD-1). Infliximab induced a dose-dependent inhibition of proliferation in both CD4 and CD8 T cells and a reduction in IFNγ production. Nivolumab induced a dose- dependent enhancement of proliferation in both CD4 and CD8 T cells and an increase in IFNγ production.
- Polyclonal – several classes of polyclonal activator can be employed in our assays, from plant-derived lectins such as phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and concanavalin A (ConA), to various anti-CD3/CD28 antibody based formats, we can advise on those best suited to your study.
Mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) – based on the reaction to mismatched HLA between unrelated donors, the stimulation of T cells by allogeneic PBMCs or monocyte-derived dendritic cells represent a flexible platform for assessment of immunomodulatory compounds. This is often used as a T cell activation assay system for immunomodulator profiling.

T Cell Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity
T cell-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (TDCC) assays measure the ability of T cells to recognise and kill target cells. This assay quantifies the cytotoxic potential of T cells in response to specific antigens or therapeutic interventions applicable to cancer research, immunotherapy development and viral infection studies.
CD3xEGFR and CD3xPSMA bi-specific T cell engagers (BiTEs) induce cytolysis in EGFR and PSMA expressing cell lines, respectively.
RoukenBio specialises in both TDCC assays and broader T cell directed cytotoxicity assays, enabling comprehensive evaluation of T cell killing mechanisms under engineered, antigen-specific, or pharmacologically modulated conditions.

Pan CD3 T cells isolated from PBMCs were incubated with target cells expressing the antigen of interest in the presence of BiTE at increasing concentrations (0 to 1 nM). xCELLigence RTCA read outs showed a clear dose-dependent effect for target cell cytolysis.
T Cell Polarisation
Various T helper activities (e.g. Th1, Th2, Th17, iTreg) are key to the orchestration of both protective and dysfunctional immune responses. Evaluate polarisation of naïve T cell populations or biases in established T cell responses via assessment of cytokine and transcription factor profiles.
Assessing CD4 T cell polarisation:

PMA/lonomycin stimulated Th1 cells produce high amounts of IFN-γ whilst Th17 cells produce IL-17A.
Treg Assays
Regulatory T cells (Tregs), a subset of CD4+T cells that constitutively express the transcription factor FoxP3 and high levels of CD25, are essential in maintaining immune homeostasis and self-tolerance. The two types of naturally occurring Tregs (nTregs) are thymus-derived Tregs (tTregs) and peripherally induced Tregs (pTregs or iTregs). Tregs contribute to many immune-mediated diseases either via the inhibition of effective immunity (e.g. in cancer and infection) or by failing to control undesirable immune responses (e.g. in autoimmunity, allergy, certain infections and transplantation). Therapeutic strategies can be employed to either inhibit or boost Treg function.
We offer a comprehensive range of regulatory T cell (Treg) assays to support your immunological research and therapeutic development. Our assays are designed to provide detailed insights into the biology and functionality of nTregs and iTregs, as well as their potential for therapeutic applications. RoukenBio has extensive experience in assessing the impact of customer molecules on the phenotype and function of Tregs, assays include:
- Phenotypic characterisation
- Suppression of conventional T cell responses
- Expansion of nTreg and differentiation of iTreg
T cell Exhaustion
Exhausted T cells (TEX) are T cells unable to function optimally due to chronic exposure to antigen. They are characterised by reduced proliferative responses to stimuli, loss of effector function and reduced cytokine secretion in comparison to their conventional, non-exhausted counterparts. These cells become addicted to the presence of antigen in what is described as ‘antigen-dependent maintenance’. When chronic antigenic stimulation is withdrawn, TEX remain dysfunctional, suggesting a commitment to the exhausted T cell state.
Exhausted T cells are involved in the pathology of cancer and chronic viral infection. Our exhausted T cell model replicates the chronic stimulation conditions leading to T cell exhaustion and can be combined with secondary functional assays such as MLR (mixed lymphocyte reaction) and cytotoxicity assays, including T cell directed cytotoxicity assays where relevant.
Example readouts include cytokine secretion, proliferation, co-inhibitory molecule expression and cytotoxicity (kinetic or flow cytometry endpoint). TEX cells express multiple checkpoint proteins and co-stimulatory molecules e.g., PD-1, LAG-3, TIM-3, CTLA-4, CD122 and CD137 and the transcription factor TOX is also upregulated. These results have been demonstrated for multiple human donors.
RoukenBio was the first CRO to develop a human in vitro T cell exhaustion model that effectively mimics the behaviour of T cells in the TME.
Gamma-Delta T Cell Assays
Gamma-delta T cells are enriched in many peripheral tissues, are activated in an MHC-independent manner and display broad functional plasticity in response to transformed/infected cells. Their ability to directly lyse target cells, co-ordinate and interact with other key immune system cells represent attractive effector functions to be harnessed in immunotherapy.
RoukenBio offers comprehensive support in assessing the impact of customer molecules on the phenotype and function of gamma-delta T cells, including T cell directed cytotoxicity assays where γδ T cell-mediated killing is evaluated.

γδ T cells isolated from PBMCs were confirmed as CD3+ Vγ9+ Vδ2+ by flow cytometry and incubated with cells expressing the antigen of interest in the presence of a bispecific T cell engager at increasing concentrations (0 to 100 pM). xCELLigence RTCA read outs showed a clear dose-dependent effect for target cell cytolysis.
T Cell Depletion Assays
Specific rare autoreactive T cell populations represent attractive targets in T cell–driven autoimmune diseases. RoukenBio can assess T cell depletion using either pan T cells or defined rare T cell populations within Fc-mediated effector function assays (ADCC, ADCP) and TDCC.
In the ADCC-driven example presented, target T cells are incubated with purified autologous NK cells for 24 hours in the presence of a Fc-competent therapeutic antibody, with pathogenic T cell depletion quantified by flow cytometry. The data demonstrates dose-dependent depletion of the target T cell population, while all other T cell populations remained intact.
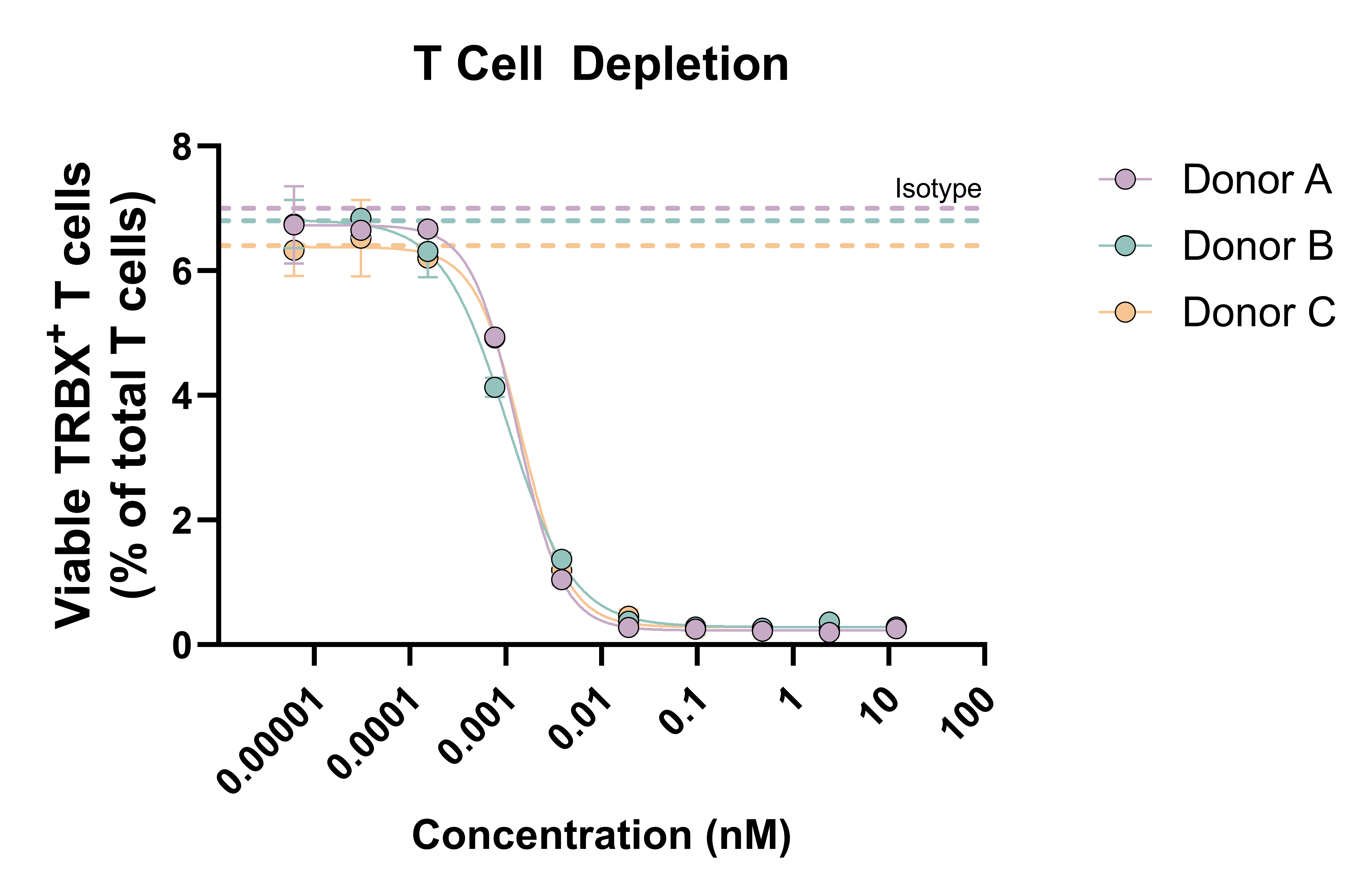 Pan T cells were incubated with purified NK cells (autologous donor) for 24 hours and T cell depletion was assessed by flow cytometry (% target expressing)
Pan T cells were incubated with purified NK cells (autologous donor) for 24 hours and T cell depletion was assessed by flow cytometry (% target expressing)
CAR-T Cell Engineering
Our CAR-T cell engineering services include the design, generation, and functional assessment of 1st to 4th generation chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. We offer comprehensive support from vector construction to in vitro testing applicable to cancer immunotherapy, personalised medicine, adoptive cell transfer research.

CAR-Ts screened in standard assays using RoukenBio's IndEx-2 inducible expression platform to determine the affect of antigen density on effector response.
Learn more about our T cell capabilities
Discover how our T cell assays can support cutting-edge immunological research and therapeutic development. Our assays are designed to provide deep insights into T cell functionality, activation, and engineering.
ACCESS THE TECHNICAL PRESENTATION